How would you answer structural elucidation question? In this post, I’ll go through step-by-step how to tackle and answer such questions tested in H2 A Level Chemistry using a sample question.
To learn the steps on how answer structural elucidation questions, read this post here.
Structural elucidation question:
In this post, let’s look at this example structural elucidation question.
Succinic acid has a structure of HOOCCH2CH2COOH. This acid can be synthesised from bromoethanal via a series of reaction.
Bromoethanal was reacted with HCN in the presence of KCN to form W, C3H4BrNO.
W was then reacted with reagent U under appropriate condition to form X, C4H4N2O.
Upon heating X with dilute hydrochloric acid, Y, C4H6O5 was generated.
It is also known that when hot acidified KMnO4 was added to Z, only an acidic gas was produced.
Deduce the structures of W, X, Y and Z, explaining the reactions described.
To go straight to the answer, click here.
You can also watch the step-by-step guide to how to answer the structural elucidation question here:
Structuring Your Answer
To do this question, we’ll format our answer in this manner which we have talked about in this post here.

In other words, we’ll need to look at the statements in the question, and come up with the deductions, and finally the structure of the unknowns (in this case compounds W, X, Y and Z).
Deductions for this structural elucidation question
Now, let’s look at each statement of the question, and see what deductions could be made.
We know we start off with bromoethanal, which has 2 functional groups, the halogenoalkane and aldehyde group:
Bromoethanal was reacted with HCN in the presence of KCN to form W, C3H4BrNO.
This is the structure of bromoethanal. There are 2 functional groups – aldehyde group and halogenoalkane group. Hence, well think of reactions involving these 2 groups.

Reaction involving HCN with trace amount of KCN is a nucleophilic addition reaction on the carbonyl group. We can also tell that it is the aldehyde group that has reacted since W still has a Br.
Since the starting compound is known, we know what W is, hence, the structure of W can also be determined from this statement.
And write the structure of W as:

W was then reacted with reagent U under appropriate condition to form X, C4H4N2O.
Now that we know the structure of W, and we know that W reacts to form X, what is this reaction and what is X?
Observing X and W, we notice that the bromine in W is gone, and there is an increase in the number of carbon increase by 1 and number of nitrogen increase by 1. This is a substitution reaction where -Br is substituted by- CN. This reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction involving halogenoalkanes. The reagents and conditions needed are ethanolic KCN and heat.
Hence, we have also deduced the structure of X.

Upon heating X with dilute hydrochloric acid, Y, C4H6O5 was generated.
We know the structure of X, and it has both the -CN (nitrile group) group and the -OH (alcohol). Heating with dilute hydrochloric acid is an acid hydrolysis reaction. From the organic reactions that you have learnt, -CN groups undergo acid hydrolysis with hot acid to form -COOH. Since the number of oxygen increases by 4, we know that both -CN groups in X are converted to -COOH.

Y was then heated with concentrated sulfuric acid to form Z which is a dicarboxylic acid with molecular formula C4H4O4.
Compare the formula of Y which is C4H6O5 and the formula of Z which is C4H4O4, there is a loss of 2 hydrogens and 1 oxygen – or in other words, loss of water (H2O). Since there is an alcohol group in Y, we’ll think of dehydration of alcohol which requires hot concentrated sulfuric acid. This dehydration of alcohol is an elimination reaction where water is eliminated, and the final product will have a C=C (alkene functional group).

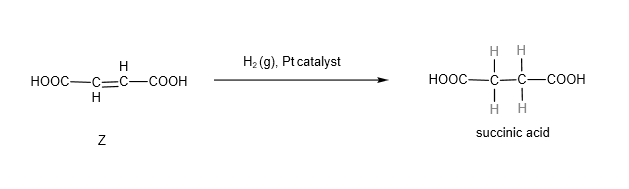
Subsequent introduction of H2(g) in the present of platinum catalyst will convert Z to succinic acid.
Since we know Z has this structure:
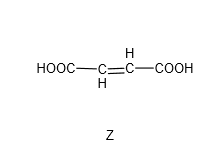
And at the start of the question, we are given the structure of succinic acid, which is HOOCCH2CH2COOH, we know that Z involves addition of hydrogen across the C=C bond (which is what hydrogen with platinum catalyst does!)
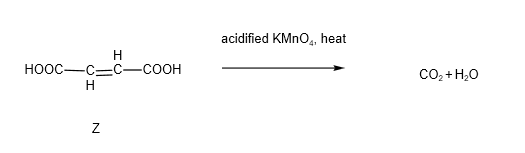
It is also known that when hot acidified KMnO4 was added to Z, only an acidic gas was produced.
You should have guessed that the acidic gas is carbon dioxide. There are 2 steps involved in the oxidation reaction. Firstly, alkenes undergo oxidative cleavage in the presence of hot acidified KMnO4, resulting in the formation of ethanedioic acid. We also learnt that ethanedioic acid is one of the acids that will be oxidised by hot acidified KMnO4 to from carbon dioxide and water.
How to Present Your Answer for this structural elucidation question
Now that we have gone through all the reactions, and found the structures of W, X, Y and Z, it’s time to present your answers.
Here’s how you can present the answer to this question:
| Statements | Deductions |
| Bromoethanal was reacted with HCN in the presence of KCN to form W, C3H4BrNO. | Nucleophilic addition of aldehyde group in bromoethanal occurs. -CN and -OH group present in W. |
| W was then reacted with reagent U under appropriate condition to form X, C4H4N2O. | halogenoalkane group (due to presence of -Br) in W undergoes nucleophilic reaction. -Br group substituted by- CN group. X has 2 -CN groups. |
| Upon heating X with dilute hydrochloric acid, Y, C4H6O5 was generated. | The two -CN groups in X are converted to -COOH group in Y in this acid hydrolysis reaction. |
| Y was then heated with concentrated sulfuric acid to form Z which is a dicarboxylic acid with molecular formula C4H4O4. | Elimination reaction. Water is eliminated. Z has a C=C. |
| Subsequent introduction of H2(g) in the present of platinum catalyst will convert Z to succinic acid. | Reduction of alkene group in Z. C=C converted to alkane . |
| It is also known that when hot acidified KMnO4 was added to Z, only an acidic gas was produced. | Oxidation of Z gives carbon dioxide gas. |
Structures:




Related Post
H2 Chemistry Courses
H2 Chemistry Books
Revision
Reactions
- Organic Chemistry Reactions Tested in H2 A Level Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry Reaction Mechanisms
- Organic Chemistry Concept Maps Part 1
- Organic Chemistry Concept Maps Part 2
- Structural Elucidation Questions

