A unit vector is a vector that has a magnitude of 1 unit.
Vectors i, j and k are examples of unit vectors, since:
- vector i is a vector in parallel to the x-axis, and has a magnitude of 1 unit
- vector j is a vector in parallel to the y-axis, and has a magnitude of 1 unit
- vector k is a vector in parallel to the z-axis, and has a magnitude of 1 unit
In Math, we put the symbol ∧ above the vector to represent a unit vector.
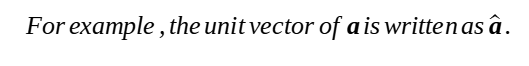
For vectors that do not have a magnitude of 1, we can divide them by their own magnitude to so that they become a unit vector.
Hence, to find the unit vector of a, we use this formula:
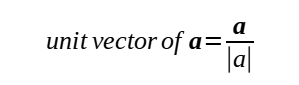
Notes on H2 Math Vectors
You’ll find all the notes on H2 A Level Math Vectors topic here.
All the notes for H2 A Level Math
Go here to find all the notes and resources for H2 A level Math.
