In this post, we’ll talk about sp³, sp² and sp orbital hybridisation.
- sp³ hybridisation
- sp² hybridisation
- sp hybridisation
sp³ hybridisation
In sp³ hybridisation, the s orbital and 3 p orbitals hybridise to form four sp³ hybridised orbials.

Here’s the shape of a hybridised orbital. Think of it as a combination of the s and p orbitals.

The bond angle between sp³ hybridised orbitals is 109.5ᵒ, and the shape is tetrahedral.
Examples of sp³ hybridisation
C in methane (CH₄), O in water (H₂O), N in ammonia (NH₃) are all sp³ hybridised.
sp² hybridisation
In sp² hybridisation, the s orbital and 2 p orbitals hybridise to form three sp² hybridised orbials.
As only three of the s and p orbitals are hybridised, one of the p orbital remains unhybridised.
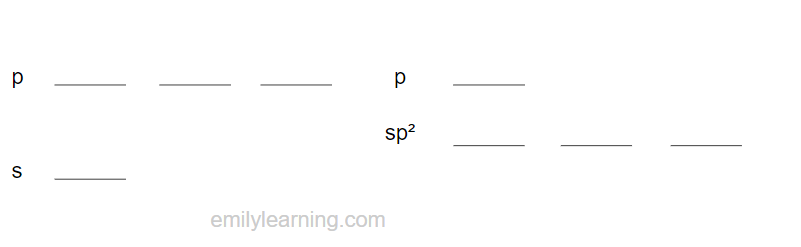
The bond angle between sp² hybridised orbitals is 120ᵒ, and the shape is trigonal planar.
Examples of sp² hybridisation
C in ethene (C₂H₄), O in oxygen (O₂) and B in boron trifluoride (BF₃) are sp² hybridised. Note that pi electrons and empty orbitals will not be in the hybridised state.
sp hybridisation
In sp hybridisation, the s orbital and 1 p orbitals hybridise to form three sp hybridised orbials.
As only two of the s and p orbitals are hybridised, two of the p orbital remains unhybridised.
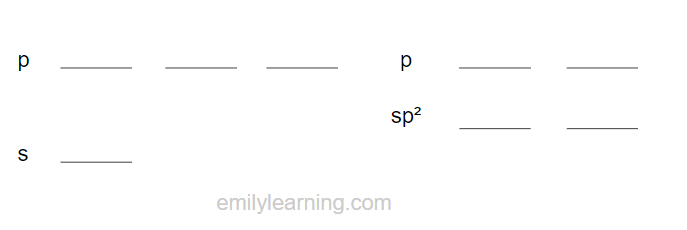
The bond angle between sp hybridised orbitals is 180ᵒ, and the shape is linear.
Examples of sp hybridisation
C in ethyne (C₂H₂), C and N of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and berrylium chloride (BeF₂) are sp hybridised. Note that pi electrons and empty orbtials will not be in the hybridised state.

