In this post, let’s look at examples of dot-and-cross diagrams of ionic compounds for O Level Chemistry. Specifically, we will only be drawing the dot-and-cross diagrams showing the electrons in the outermost shell.
The dot-and-cross diagrams of ionic compounds that we will be looking at will be these:
- sodium chloride
- sodium oxide
- magnesium chloride
- magnesium oxide
- aluminium oxide
- more on dot-and-cross diagrams
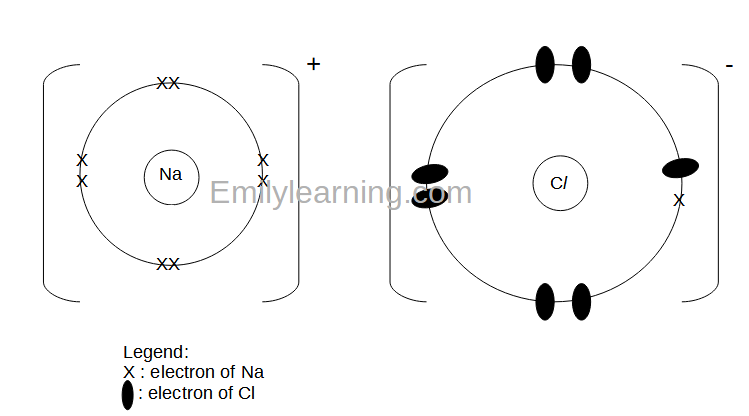
Dot-and-Cross Diagram 1 of Ionic Compound: Sodium Chloride
To draw the dot-and-cross diagram of sodium chloride, let’s first determine its formula. Since sodium is in group I of the periodic table, it forms ions with charge of +1. Chlorine is in group VII of the periodic table, it forms ions with charge of -1. With that, the formula of sodium chloride is NaCl.
A sodium atom has 11 electrons. A sodium ion which has a charge of +1 will have 10 electrons. Sodium ion has an electronic configuration of (2,8). We will draw 8 electrons in the valence shell for sodium ion.
A chlorine atom has 17 electrons. A chloride ion has a charge of -1, and will have 18 electrons. Chloride ion has an electronic configuration of (2,8,8). We will also draw 8 electrons in the valence shell of chloride ion. Since the valence electrons are in the 3rd principal quantum shell for chloride, compared to the 2nd principal quantum shell for the valence electrons of sodium ion. Hence, we should draw the valence shell of chloride ion bigger than the valence shell of sodium ion.
Dot-and-Cross Diagram 2 of Ionic Compound: Sodium Oxide
To draw the dot-and-cross diagram of sodium oxide, let’s first determine its formula. Since sodium is in group I of the periodic table, it forms ions with charge of +1. Oxygen is in group VI of the periodic table, it forms ions with charge of -2. With that, the formula of sodium chloride is Na2O.
A sodium atom has 11 electrons. A sodium ion which has a charge of +1 will have 10 electrons. Sodium ion has an electronic configuration of (2,8). We will draw 8 electrons in the valence shell for sodium ion.
An oxygen atom has 8 electrons. An oxide ion has a charge of -2, and will have 10 electrons. Oxide ion has an electronic configuration of (2,8). We will also draw 8 electrons in the valence shell of oxide ion.
Both valence electrons of oxide ion and sodium ion are in 2nd principal quantum shell, hence they should be of the same size.

Dot-and-Cross Diagram 3 of Ionic Compound: Magnesium Chloride
To draw the dot-and-cross diagram of magnesium chloride, let’s first determine its formula. Since magnesium is in group II of the periodic table, it forms ions with charge of +2. Chlorine is in group VII of the periodic table, it forms ions with charge of -1. With that, the formula of sodium chloride is MgCl2.
A magnesium atom has 12 electrons. A sodium ion which has a charge of +2 will have 10 electrons. Magnesium ion has an electronic configuration of (2,8). We will draw 8 electrons in the valence shell for magnesium ion.
A chlorine atom has 17 electrons. A chloride ion has a charge of -1, and will have 18 electrons. Chloride ion has an electronic configuration of (2,8,8). We will also draw 8 electrons in the valence shell of chloride ion.
Since the valence electrons are in the 3rd principal quantum shell for chloride, compared to the 2nd principal quantum shell for the valence electrons of magnesium ion. Hence, we should draw the valence shell of chloride ion bigger than the valence shell of magnesium ion.

Dot-and-Cross Diagram 4 of Ionic Compound: Magnesium Oxide
To draw the dot-and-cross diagram of magnesium oxide, let’s first determine its formula. Since magnesium is in group II of the periodic table, it forms ions with charge of +2. Oxygen is in group VI of the periodic table, it forms ions with charge of -2. With that, the formula of sodium chloride is MgO.
A magnesium atom has 12 electrons. A sodium ion which has a charge of +2 will have 10 electrons. Magnesium ion has an electronic configuration of (2,8). We will draw 8 electrons in the valence shell for magnesium ion.
An oxygen atom has 8 electrons. An oxide ion has a charge of -2, and will have 10 electrons. Oxide ion has an electronic configuration of (2,8). We will also draw 8 electrons in the valence shell of oxide ion.
Both valence shells of oxide ion and magnesium ion are in 2nd principal quantum shell, hence they should be of the same size.

Dot-and-Cross Diagram 5 of Ionic Compound: Aluminium Oxide
To draw the dot-and-cross diagram of aluminium oxide, let’s first determine its formula. Since aluminium is in group III of the periodic table, it forms ions with charge of +3. Oxygen is in group VI of the periodic table, it forms ions with charge of -2. With that, the formula of sodium chloride is Al2O3.
An aluminium atom has 13 electrons. An aluminium ion which has a charge of +3 will have 10 electrons. Aluminium ion has an electronic configuration of (2,8). We will draw 8 electrons in the valence shell for aluminium ion.
An oxygen atom has 8 electrons. An oxide ion has a charge of -2, and will have 10 electrons. Oxide ion has an electronic configuration of (2,8). We will also draw 8 electrons in the valence shell of oxide ion.
Both valence shell of oxide ion and aluminium ion are in 2nd principal quantum shell, hence they should be of the same size.

Learn O Level Chemistry topics on-demand
Want this topic and other topics tested in the O Level Chemistry (Pure) syllabus? Check out our On-demand chemistry courses written based on the Singapore O Level Chemistry syllabus.

